1. Overview
The electronics industry is the core of high-tech today, and it has played a huge role in the development of human technology. The electronics industry has become the fastest-growing high-tech industry in the world today, playing a crucial role in the national economy of countries around the world. Today's electronic technology cannot do without integrated circuits, which are the cornerstone of the electronics industry and one of the greatest inventions of the 20th century.
Integrated circuit is a type of microelectronic device or component. It uses a certain process to interconnect the required components and wiring in a circuit, and then makes them on a small substrate, and then packages them in a tube shell, where all components are structurally integrated into a whole. Integrated circuits include semiconductor integrated circuits and hybrid integrated circuits.
Semiconductor integrated circuit is the use of semiconductor technology to manufacture components and wiring such as resistors, capacitors, inductors, transistors, etc. in the same semiconductor material, forming a complete and independent functional circuit system.
Hybrid integrated circuit is the process of solidifying multiple different semiconductor integrated circuits and discrete electronic components onto the same substrate (ceramic or semiconductor material) through microfabrication technology, and integrating them into a complete, independent functional circuit system through interconnection.
This article mainly introduces the knowledge and technology related to semiconductor integrated circuits.
Classification of Semiconductor Integrated Circuits
Integrated circuits can be divided into digital integrated circuits, analog integrated circuits, and mixed signal integrated circuits according to their functions.
Digital integrated circuit refers to a type of circuit that only processes digital signals, also known as logic circuit. This type of product mainly includes microprocessors (MPUs), microcontrollers (MCUs), memory (RAM, ROM), interface circuits, etc. Digital integrated circuits are typically composed of basic logic gate circuit units.

**Analog integrated circuit refers to a type of circuit that amplifies, converts, modulates, and performs operations on analog signals** Due to the fact that these types of circuits were mainly used for linear signal processing in the early days, they are also known as linear circuits. Analog integrated circuits include amplifiers, analog multipliers, analog switches, and power supply circuits.
2. Development of Integrated Circuits
Why was integrated circuit invented?
What can it bring us?
We will unravel the driving force behind the invention and creation of semiconductor integrated circuits through the development history of semiconductor integrated circuits.
drive
In 1946, ENIAC (Electronic Numerical integrator and computer) was announced to be born in the United States. ENIAC was the second electronic computer after ABC (Atanasoff Berry computer), and the US Department of Defense used it to calculate trajectories. ENIAC could perform 5000 calculations per second. ENIAC is a behemoth! ENIAC has a total length of about 30 meters, a height of about 4 meters, a thickness of about 0.9 meters, covers an area of about 167 square meters, and weighs 30 tons! The internal circuit of ENIAC uses about 18000 tubes, 7200 resistors, 10000 capacitors, 500000 wires, and a power of about 150 kilowatts.
Electronic computers provide unparalleled computing power, but they have several prominent issues: large size and high power consumption. If the electronic components and wiring inside the computer can be integrated on a small carrier, this will solve the problems of volume and power consumption! The intrinsic driving force behind the birth and development of semiconductor integrated circuits lies in this!
development
On December 23, 1947, William Shockley and John Bardeen from Bell Laboratories in the United States invented the point touch transistor, which was the world's first crystalline transistor. It marked the first step in electronic technology from the era of electronic tubes to the era of transistors!
Prior to this, computer circuits could only use electronic tubes with large volume, high power consumption, and unstable structure. Transistors have the main functions of electronic tubes, while solving problems such as large size, high power consumption, and unstable structure. After the invention of the transistor, Shockley published "Theory of P-N Junction and P-N Junction Transistors in Semiconductors" in internal publications at Bell Laboratories in 1948, and "Electrons and Holes in Semiconductors" in November 1950, laying the foundation for the basic theory of PN junction and junction transistors.
In 1954, Texas Instruments purchased a patent for producing electronic transistors from Western Electronic Company for $25000 and developed the first commercial silicon transistor 905 in the same year. Texas Instruments became the only company at the time to mass produce silicon transistors.

In 1958, Kilby of Texas Instruments had a sudden idea: tiny microcircuits composed of many components could be fabricated on a single chip. On September 12, 1958, Kilby turned this idea into reality and developed the world's first integrated circuit (which was actually an integrated circuit consisting of only 12 components). With this invention, Kilby won the Nobel Prize in Physics in 2000.
In 1959, Bob Noyce (later the founder of Intel at Fairchild Semiconductor Company), who was working at Fairchild, created the mask plate exposure etching method for producing integrated circuits.
In 1964, Gene Amdahl, who was only forty years old at IBM, served as the chief designer and spent four years developing the IBM360 computer. The IBM360 was the world's first integrated circuit computer built using integrated circuits, also known as the third generation computer. This computer has six models, large, medium, and small, covering both scientific computing and transaction processing applications, and can be used 360 degrees in all directions. Therefore, it is named IBM360. The biggest feature of this computer compared to previous ones is that it has shifted from military use to civilian use, representing the comprehensive application of computers from the business and scientific communities.
In 1970, Intel scientist Ted Hoff led the design of the world's first microprocessor, the Intel 4004. The Intel 4004 chip integrates 2250 transistors with a distance of 10 microns between them, capable of processing 4 bits of data, performing 60000 operations per second, and supporting 8-bit instruction sets and 12 bit address sets.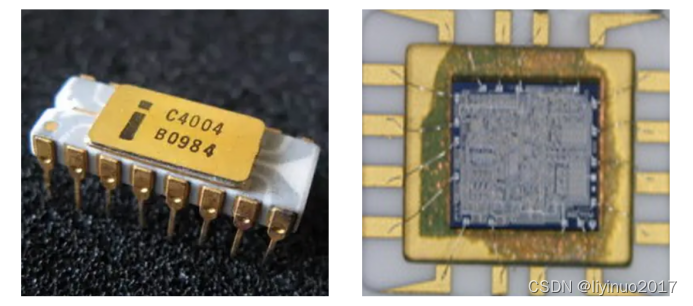
In June 1978, Intel launched the 8086 microprocessor, which was the pioneer of x86 architecture microprocessors. All subsequent microprocessors were compatible with it. The 8086 has a working frequency of 4.77MHz and uses 16 bit registers and a 16 bit data bus. The 8086 microprocessor uses a+5V power supply, a 40 pin dual in-line package, 16 data lines and 20 address lines, and implements segmented management of memory space to address 1MB space. It adopts a parallel pipeline working mode. 8086 is a groundbreaking microprocessor.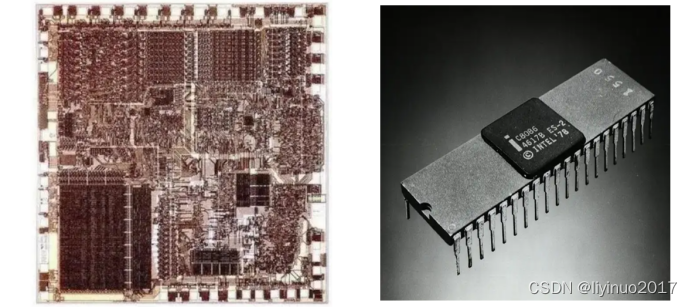
In 1993, Intel released the Pentium series microprocessor 80586, which is fully compatible with previous Intel processors. It is worth mentioning that the Pentium processor has two data pipelines that can execute two instructions simultaneously. Intel Corporation refers to this ability to execute two instructions simultaneously as superscalar technology. The first generation Pentium processor has clock speeds of 60MHz and 66MHz.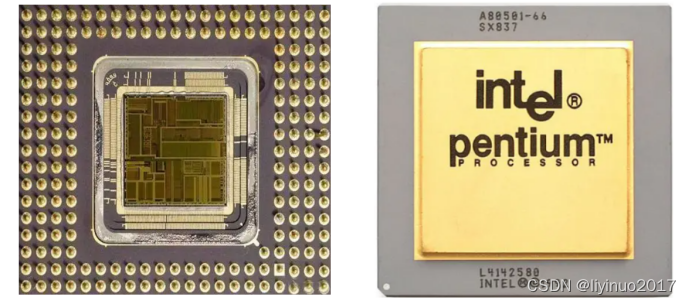
On August 31, 2018, Huawei released the Kirin 980 chip at the IFA exhibition in Berlin, Germany. The Kirin 980 chip is a 64 bit system chip based on ARM launched by Huawei HiSilicon. It is the world's first commercial mobile SoC chipset (4A76+4A55 eight core chip) manufactured using TSMC's 7nm process, with a maximum clock frequency of up to 2.8GHz. The Kirin 980 integrates eight CPU cores, ten GPU cores, dual ISP, i8 sensor processor, security engine, and supports UFS 2. Hi Fi audio and 4K video.
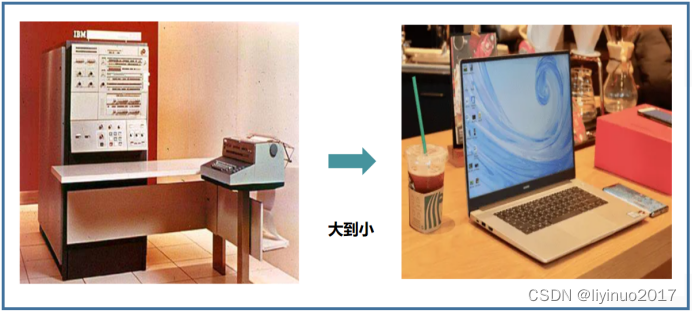
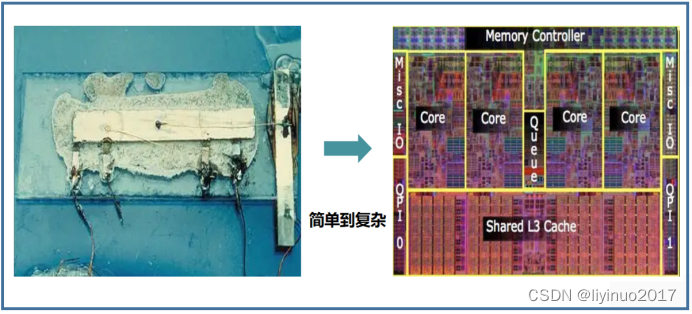
Looking at the development of semiconductor integrated circuits, two trends can be summarized:
1. The volume is getting smaller and smaller.
2. The functions are becoming increasingly complex.
3. Integrated circuit materials
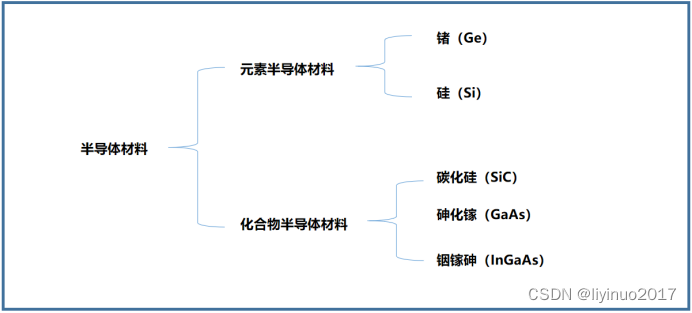
3.1 Semiconductor Materials
Semiconductor materials are the main materials used in the manufacturing of semiconductor integrated circuits. Currently, there are two types of semiconductor materials used in integrated circuits: elemental semiconductors and compound semiconductors. Elemental semiconductors mainly include germanium (Ge) and silicon (Si). Compound semiconductor materials include silicon carbide (SiC), gallium arsenide (GaAs), indium gallium arsenide (InGaAs), etc.
3.2 Characteristics of Semiconductor Materials
Semiconductor integrated circuits are mainly manufactured using semiconductor materials. The reason why extremely complex semiconductor integrated circuits can be manufactured using semiconductor materials is because semiconductors have a series of characteristics: conductivity, doping, temperature, photoelectric, pressure, etc.
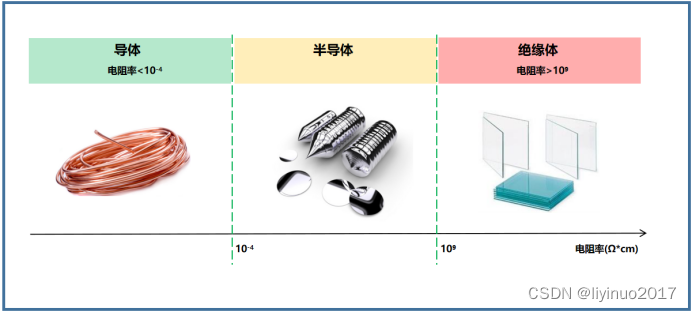
Conductive properties
The strength of a substance's conductivity is represented by its conductivity, and the reciprocal of conductivity is called resistivity. According to the magnitude of resistivity, substances in nature can be divided into three categories: conductors, semiconductors, and insulators. Among them, the resistivity of semiconductors is between that of conductors and insulators, as shown in the following figure:
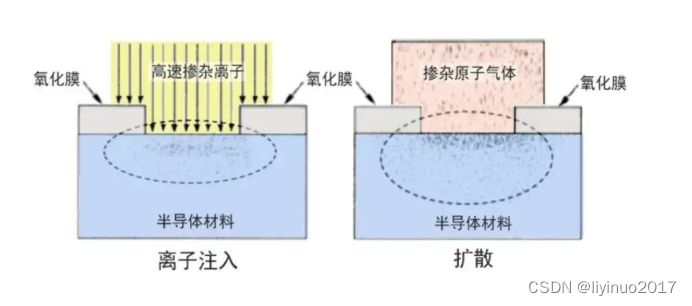
Doping characteristics
Adding trace amounts of other elements to semiconductor materials, known as doping, can greatly alter the conductivity of semiconductors. Taking semiconductor material silicon as an example, the resistivity of pure silicon at room temperature is 230000 Ω* cm. However, as long as 0.000001% (one millionth) of phosphorus element is added, the conductivity of silicon material containing impurities will be increased by 20000000% (200000 times)! It can be seen that although the content of doping elements is extremely small, it plays a decisive role in the conductivity of semiconductors.
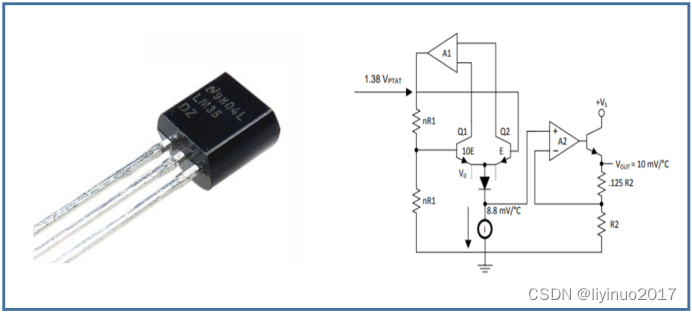
temperature characteristic
Semiconductors have an important characteristic of increasing carrier concentration and decreasing resistance with increasing temperature. By utilizing this effect of semiconductors, semiconductor thermistors can be made. With the continuous development of semiconductor integrated circuit technology, semiconductor integrated temperature sensors are receiving increasing attention from people. Semiconductor integrated temperature sensors have advantages such as smaller size and easy system integration. This integrated temperature sensor integrates temperature sensing devices, ADC circuits, and digital circuits together, which can output digital signals and be easily processed in a microprocessor. The semiconductor integrated temperature sensor mainly uses BJT as the temperature measurement device. The following is the functional block diagram of the semiconductor temperature sensor LM35:
Photoelectric characteristics
Semiconductor materials can increase their conductivity by hundreds of times when exposed to light, and this effect can be utilized to create semiconductor optoelectronic sensors: photo diodes. A photodiode is a semiconductor device composed of a PN junction with unidirectional conductivity. Photodiodes work under the action of reverse voltage, and the current generated under normal illumination is called photocurrent. If a load is connected to the external circuit, an electrical signal is obtained on the load, and this electrical signal changes accordingly with the variation of light. The photoelectric sensor is shown in the following figure:
Pressure characteristics
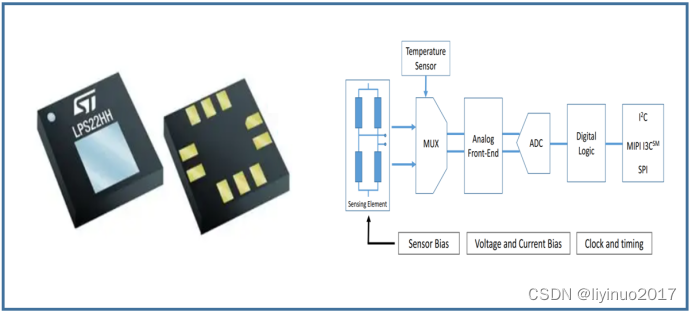
When a semiconductor is subjected to stress, the change in energy band caused by stress results in a change in its resistivity, a physical phenomenon known as the piezoresistive effect. By utilizing this effect of semiconductors, semiconductor pressure sensors can be made, which have a simple and reliable structure without relative moving parts. The elastic element and pressure sensitive element in the sensor are integrated, improving the performance of the sensor. The following is the functional block diagram of the semiconductor pressure sensor LPS22HH:
3.3 Semiconductor and Impurity Semiconductor Certificates
Intrinsic semiconductor
A pure semiconductor material without any impurities or defects is called an intrinsic semiconductor, and the conductivity characteristics of this semiconductor depend on the inherent properties of the material itself.
Impurity semiconductor
The semiconductor materials used in integrated circuits are not genuine semiconductors, but rather impurity semiconductors. The semiconductor doped with a certain amount of other elements in this certificate is called an impurity semiconductor. The impurities doped are called impurity atoms, and the process of doping impurity atoms is called doping. After doping impurities into pure semiconductor materials, the conductivity of the semiconductor will undergo significant changes.
N-type semiconductor
After doping trace amounts of trivalent elements such as phosphorus (P), arsenic (Sb), antimony (As), etc. into semiconductor materials, many negatively charged electrons will be generated, resulting in a much higher concentration of free electrons than holes in the semiconductor. These types of impurities provide negatively charged electron carriers, hence they are called N-type impurities, and this type of semiconductor is called N-type semiconductor. For N-type semiconductor materials, the total positive charge is equal to the number of negative charges, and the material as a whole is electrically neutral.








 P型半导体
P型半导体